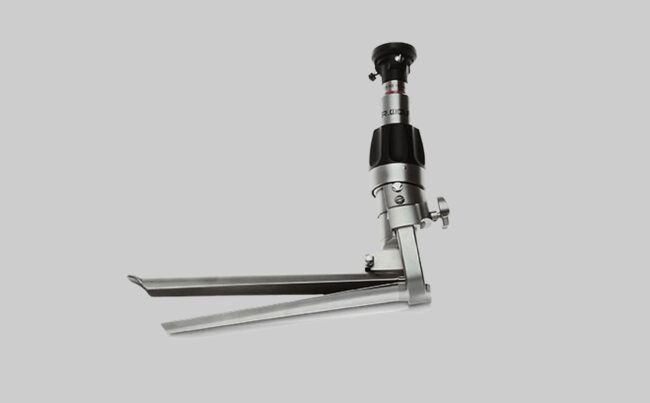
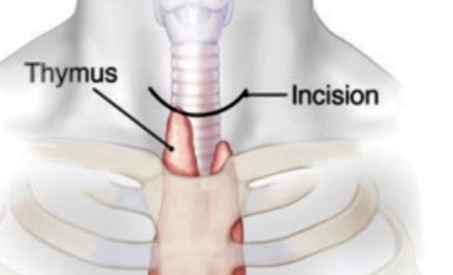
Mediastinoscopy
Many surgical or non-surgical procedures have been described and used for the diagnosis and treatment of lung diseases. Mediastinoscopy is particularly in one of these methods, which are currently being implemented and developed by only thoracic surgeons. Surgeons, who perform more demanding operations during the specialist training, might not find an adequate basis in hospitals…